What’s an OS kernel? Types of Kernels? No matter if it’s Windows, Mac, Linux, or Android, each operating system has a main program called a Kernel that runs everything. It’s what the OS is made of! The Kernel is just a computer program that walks through everything and keeps it running. It sees all the things that happen on the computer. We will talk about what an OS Kernel is and the various types of Kernels in this post.
What is a Kernel in OS
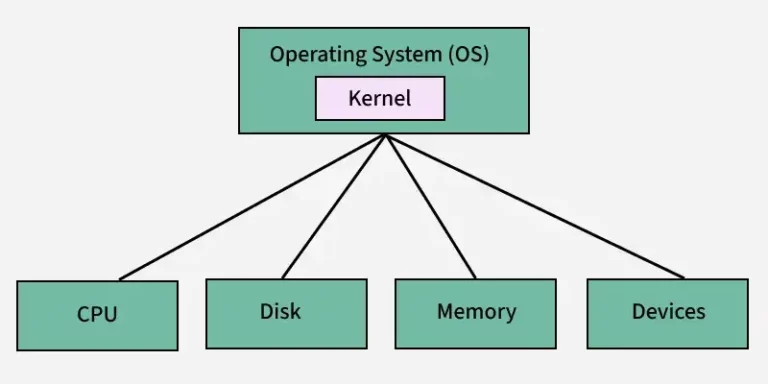
We now know that it is an important part of the OS and that it is the first program that starts after the bootloader. Once that’s done, it talks between the hardware and the software or apps. The user interface makes a request to Kernel when you start a program. In order for the program to run smoothly in the front end, the Kernel then makes a request to the CPU and Memory to allocate processing power, memory, and other resources.
Kernel could be thought of as a translator. It takes input and output requests from software and turns them into a set of instructions that the CPU and GPU can follow. It’s a layer that sits between the hardware and the software and makes everything work.The kernel is in charge of these things:
- CPU/GPU
- Memory
- Input/Output or IO devices
- Resource management
- Memory management
- Device management
- System calls.
System calls are the only way that user apps can reach kernel space. If a program tries to get to it directly, an error will happen.
Kernel Security & Protection
The kernel also keeps the hardware safe. There will be no protection if there isn’t any. Any program can do anything on the computer, even crash it or mess up your data.
Today’s computers have security built right into the hardware. For instance, Windows won’t load drivers that don’t come from a trusted source and have a signature to prove it. Secure Boot and Trusted Boot are two well-known examples.
Secure Boot is a security standard that was made by people who work in the PC business. By not letting any unapproved programs run during the system start-up process, it helps you keep your system safe from viruses. The feature ensures that only software that is trusted by the PC maker is used when your PC starts. So, every time your PC turns on, the firmware checks the signature of all the boot software, such as the operating system and firmware drivers (Option ROMs). The computer starts and the firmware gives the operating system control if the signatures are confirmed.
The Virtual Trusted Platform Module (VTPM) is used by Trusted Boot to check the digital signature of the Windows 10 kernel before starting it. After that, it checks every other part of the Windows starting process, such as the ELAM, boot drivers, and launch files. In the event that a file has been changed in any way, the driver will recognize it as a damaged component and refuse to load it. In short, it gives all the parts during boot a way to trust each other.
What are the types of Kernel
There is also a safe way for the Kernel to talk to hardware. They can then make a Kernel that can talk to their hardware through a set of buttons. Let’s look at the washing machine. A simple level of Kernel should be enough, depending on how you move the knobs and how long you set the time. However, the complexity of Kernels increases over time, which results in different types of Kernels.
- Monolithic Kernel: The OS and Kernel run in the same memory area. This type of kernel is good when security is not a big deal. It results in quicker access, but if the device driver has a bug, the whole system crashes.
- Some features of Monolithic Kernel have been taken out to make Microkernel. The Kernel can do most of the work itself, so there is no need for an extra GUI. They should be used in places where security and system crashes won’t happen or won’t happen at all.
- This is the Kernel that we see the most. Apple’s macOS and Windows. There are parts of both Monolithic Kernel and Microkernel in them. It gets rid of drivers but leaves system services in the Kernel. This is similar to how drivers are loaded when Windows starts to boot up.
- Nano Kernel: This is used when you need a kernel but most of its functionalities are set up outside.
- Process protection and resource management are the only features of Exo Kernel. However, it is mostly used to try an internal project and then switch to a better Kernel type.
A Kernel is more than what we’ve talked about so far. As you learn more, the word “Kernel” takes on a wider and deeper meaning.
We hope the post was clear and helps you learn the basics.